When is this recommended by the CDC? It can be given as early at 2 month, and is recommended at 11-12 years and again at 16 years. (cdcschedule) It is a little confusing so here is some info about when it can be given from the insert.

Meningococcal meningitis is a rare but serious bacterial infection. It causes the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord to become inflamed. Each year, approximately 1,000 people in the U.S. get meningococcal disease, which includes meningitis and septicemia (blood infection). (Webmed)
Doctors call meningitis caused by the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis meningococcal meningitis. When someone has meningococcal meningitis, the bacteria infect the lining of the brain and spinal cord and cause swelling. The most common symptoms include: Fever, headache, stiff neck. (cdc.gov)
Webmed said there were about 1000 cases a year in the US….Let’s see if I can find more info about that. In the US, the rate per 100,000 has become very close to 0 cases.
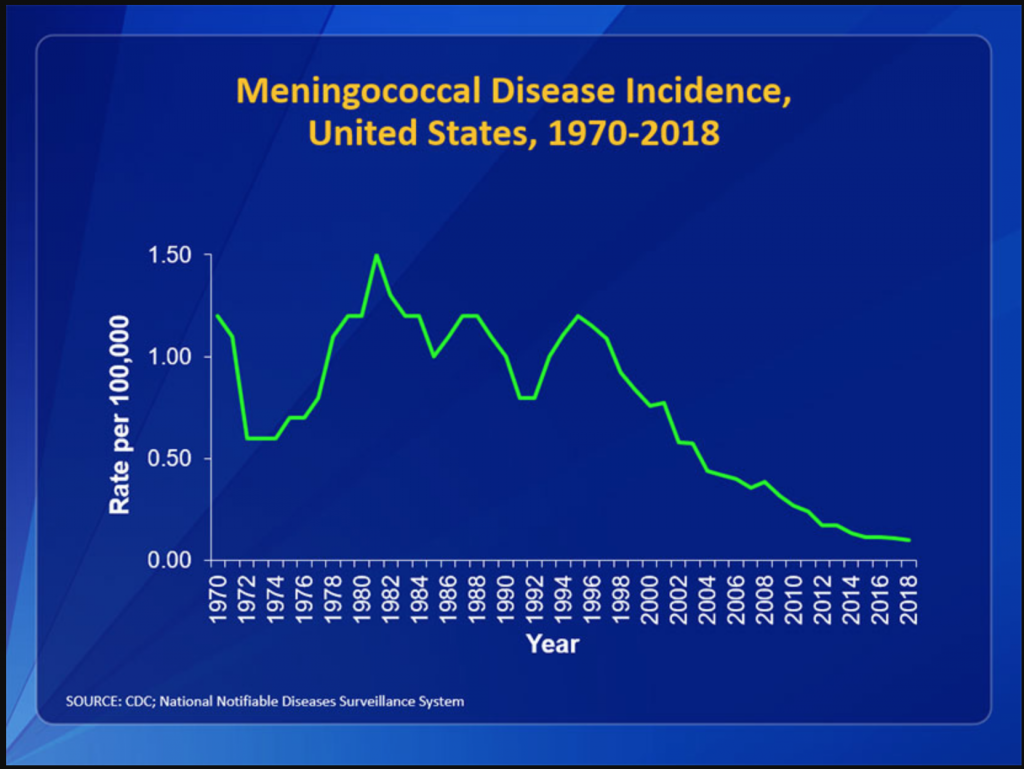
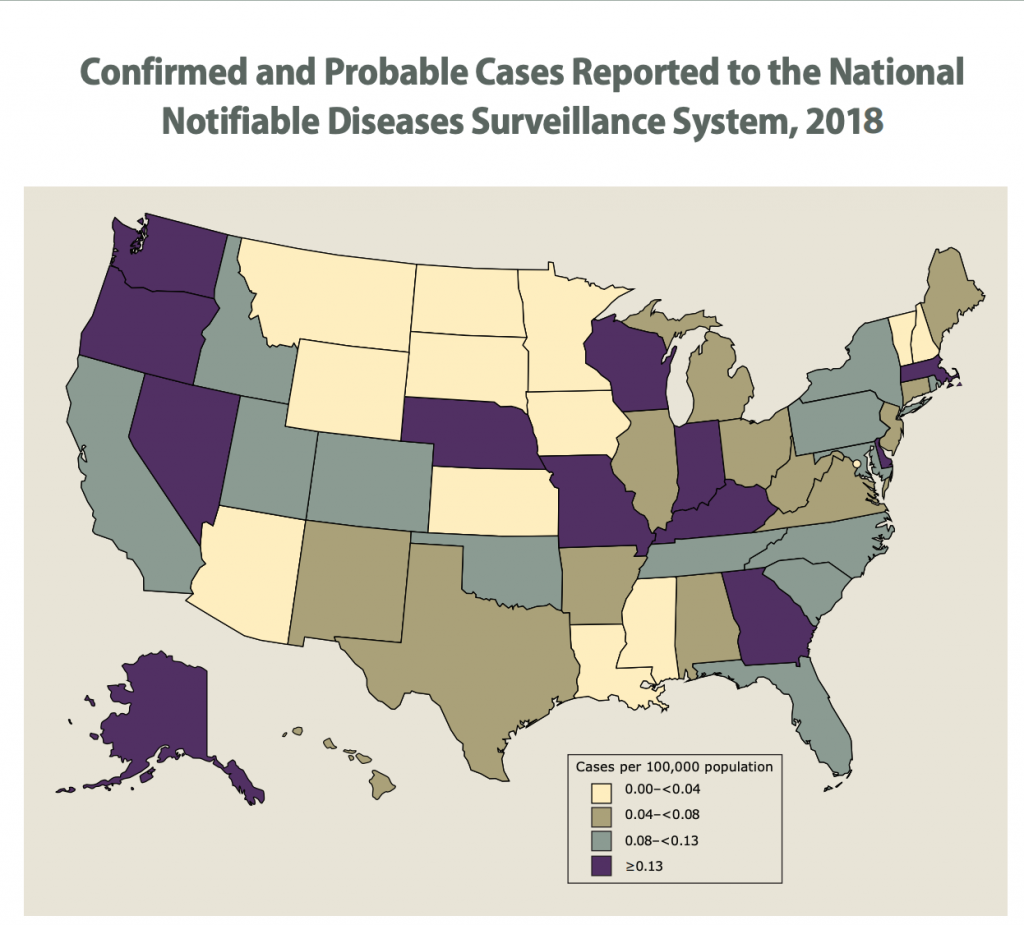
As you can see from the graph below from 2018 many states had a very low incidence of this 0.00-0.04 per 100,000 people or up to 0.4 per 1,000,000 or 4 per 10,000,000 or 1 in 2,500,000. In the highest incidence states it is greater than 0.13 per 100,000 or greater than 13 people per 10,000,000. Still seems like the most likely states where you could contract meningococcal, you still have a pretty low chance of getting it. (cdcmeningococcalreport2018)
So now let’s take a look at the vaccine insert. There are multiple meningococcal vaccine so we will just look at the insert for the following vaccine.
“Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose of MENVEO, any component of this vaccine, or any other CRM197-, diphtheria toxoid-, or meningococcal-containing vaccine is a contraindication to administration of MENVEO.” (Menveoinsert)
“Syncope, sometimes resulting in falling injury associated with seizure-like movements, has been reported following vaccination with MENVEO. Vaccinees should be observed for at least 15 minutes after vaccine administration to prevent and manage syncopal reactions.” (Menveoinsert)

Was this vaccine tested against a true saline placebo or another similar vaccine? “The safety of MENVEO in children aged 2 through 10 years
was evaluated in 4 clinical trials 6-9 conducted in North America (66%), Latin America (28%), and Europe (6%) in which 3,181 subjects received MENVEO and 2,116 subjects received comparator vaccines (either Meningococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine, Groups A, C, Y, and W135 Combined – MENOMUNE, Sanofi Pasteur [n = 861], or Meningococcal (Groups A, C, Y,
and W-135) Polysaccharide Diphtheria Toxoid Conjugate Vaccine – MENACTRA, Sanofi Pasteur [n = 1,255]).” (Menveoinsert)
How can you truly assess the safely of a meningococcal vaccine when it is tested against another meningococcal vaccine? HMM that definitely raised a red flag in my mind, and it should for you too.
“The proportions of infants randomized to receive the 4-dose series of MENVEO concomitantly with routine vaccinations and infants who received routine vaccinations alone that reported serious adverse events during different study periods were, respectively: a) 2.7% and
2.2% during the infant series, b) 2.5% and 2.5% between the infant series and the toddler dose, c) 0.3% and 0.3% in the 1 month following the toddler dose, and d) 1.6% and 2.2% during the 6- month follow-up period after the last dose.” (Menveoinsert)
To me 2.7% (who got Menveo AND routine immunizations) and 2.2% (who only routine immunizations, no Menveo) that had a serious adverse reaction, THAT IS REALLY HIGH chance of a serious adverse reaction from vaccines!!!
“MENVEO has not been evaluated for carcinogenic or mutagenic potential, or for impairment of male fertility in animals.” (Menveoinsert)
Finally here are the ingredients in the different Meningococcal vaccines
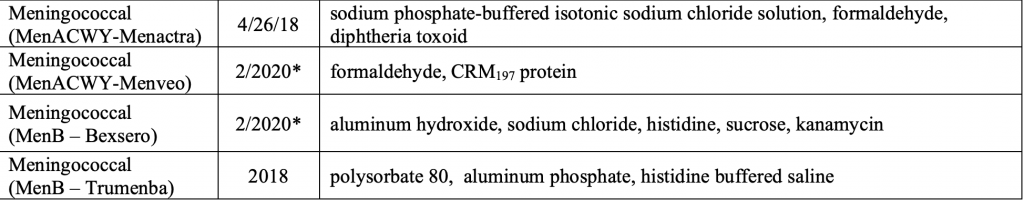
I hope this has helped give you more understanding about Meningococcal so that you can research it more and make an informed decision.